On 24th October, Dr. Xianliang Wang, a medical physicist from the radiation oncology department of Sichuan Cancer Hospital presented his latest joint research with PVmed to physicians and other physicists attended the annual meeting of Chinese Association for Therapeutic Radiation Oncologists. His research is about using Artificial Intelligence (Deep Learning) to perform OARs (organ at risk) and CTV (clinical target volume) delineation on CT images automatically. He highlighted that new technology like Deep learning is applicable to boost radiotherapy treatment Planning and improve patient outcomes.

Dr. Wang gave presentation to the attendees.
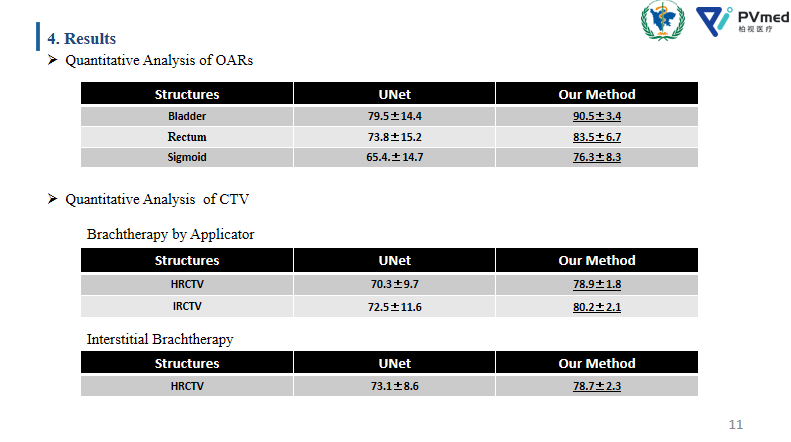
Segmenting or contouring has been considering a time-consuming and demanding task in radiation therapy. When it comes to cervical cancer brachytherapy, it becomes much sophisticated as the invasive areas of tumors and source placements need to be considered. Therefore, seeking a new method to streamline this job is necessary. Dr. Wang with PVmed proposed an AI-based model with data of 86 patients to be trained and validated, which can contour HRCTV (high-risk CTV) and IRCTV (Inter-medium CTV) for interstitial Brachytherapy, HRCTV for Brachytherapy by applicator, and OARs (bladder, rectum, sigmoid colon) for both. The metric used to evaluate this model is the DSC value that is a number to see how overlap or how close between the results generated with a standard which in this case is manual contouring conducted by experienced radiation oncologists. Higher DSC indicates a higher similarity to the standard. The DSC of bladder, rectum, and IRCTV are relatively high, and the rest are still in an acceptable range. Compared to the UNet model, a common neural network in the industry, the proposed method is competitively stable and better. It is worth mentioning in this study that they only use a small amount of data with CT images only without MRI, and if they enlarge the data and take MRI into account, the DSC value would be much higher, meaning more appreciated by the clinicians. Still, this study proves the potential of AI applications in radiation oncology.
Contouring Results
In addition to other radiotherapy methods, Proton and Heavy Ion therapy were popular topics of the meeting. For example, Dr. Xiaomao Guo from Fudan University Attached Tumor Hospital shared the evidences of 5-year Proton/Ion therapy survival rates in their hospital that these two treatments are more effective in killing the cancers than other modalities in some circumstances. These reports all emphasized the increasing preciseness in radiotherapy in the future, and the innovations from AI might be useful.

Physicians from different hospitals visits PVmed booth.

Dr. Wang with PVmed sales representatives
In the medical domain, PVmed has launched an intelligent contouring system to automatically contour the OARs, CTV, and GTV for NPC, lung cancer, cervical cancer, rectum cancer, and breast cancer. Soon, the company will cover the auto treatment planning and dose calculation to augment the whole process of radiation oncology.